- AdventHealth
International Collaborative Research Review Article Published in Drug Discovery Today
Sarfraz Ahmad, PhD
AdventHealth Cancer Institute
Ganji P. Nagaraju1, Prameswari Kasa2, Begum Dariya3, Nagalakshmi Surepalli4, Sujatha Peela5, Sarfraz Ahmad6
1Department of Hematology & Medical Oncology, Winship Cancer Institute, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30332, USA; 2Dr L. V. Prasad Diagnostics & Research Laboratory, Khairtabad, Hyderabad 500004, India; 3Department of Biosciences & Biotechnology, Banasthali University, Banasthali 304022, India; 4Dr. B. R. Ambedkar Open University, Hyderabad 500033, India; 5Department of Biotechnology, Dr. B..R. Ambedkar University, Srikakulam 532410, India; 6AdventHealth Cancer Institute, Orlando, FL 32804, USA
Gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies account for substantial mortality and morbidity worldwide. GI cancers are complex disease, resulting from genetic, epigenetic alterations, and environmental factors. They are generally promoted by dysregulated signal transduction and epigenetic pathways, which are controlled by specific enzymes.
Recent studies demonstrated that histone deacetylases (HDACs) together with DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) have crucial roles in the signal transduction/epigenetic pathways in GI regulation. In this review, we discuss various enzyme targets and their functional mechanisms responsible for the regulatory processes of GI malignancies. We also discuss the epigenetic therapeutic targets that are mainly facilitated by DNMT and HDAC inhibitors, which have functional consequences and clinical outcomes for GI malignancies. Our review also highlights foundation for future research with novel epigenetic biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and for insights into clinical interventions. Moreover, targeting the dysregulated epigenetic mechanism could assist with this by overwhelming cancer heterogeneity and promoting the reprogramming of cancer homeostasis. This potentiates efficacy and improves cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs and immune checkpoint inhibitors when used with epigenetic strategies.
Additionally, epigenetic profiling is essential for prognostic and predictive biomarkers, which can be used as a supportive aid for current diagnostic and therapeutic strategies that predict the response of the drug. However, the complexity of epigenetic molecular mechanisms reflects a substantial challenge and necessitates detailed study of the cellular environment and the array of therapeutic targets.
Highlights
- Discusses the epigenetics in GI cancers
- Explores the metastatic role(s) of epigenetics in GI cancers
- Presents epigenetics as biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of GI cancers
- Epigenetics as therapeutic solutions for GI cancers
For more information or to refer a patient, call one of our Gastrointestinal Oncology Nurse Navigators: Erica Corcoran, MSN, RN, OCN, AOCNS, ONN-CG, at Call407-303-5981, or Wyntir Purtha, BSN, RN, OCN, at Call407-303-5959.
Read the article: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1359644621002026
Recent News
The AdventHealth Neuroscience Institute is the first in Florida and one of the first in the country to begin recruiting patients with primary progressive or non-active secondary progressive multiple...
Accurately determining food intake remains a challenge in nutrition research. A new study published in Nature Metabolism and co-authored by Dr. Corbin introduces a metagenomics-powered approach to...

Discover what’s being accomplished in Central Florida to bridge the health gap with Orange County Mayor Jerry Demings and AdventHealth’s Dr. Alric Simmonds.
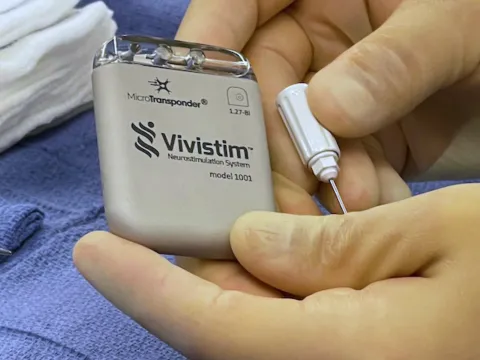
Breakthrough device offers new hope for stroke survivors struggling with rehabilitation following ischemic stroke
Jennifer Seminerio, MD, recently became one of the first in Florida to use intestinal ultrasound (IUS) to help assess and manage treatment of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). A non...
The Convergent Hybrid Ablation procedure has been gaining acceptance as an effective treatment option for long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation (AFib) since the CONVERGE trial data published in...

Recently, AdventHealth for Children pediatric orthopedic surgeon Sean Keyes, DO, Katelyn Smith, PA-C, and their team performed their 100th bridge-enhanced anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) repair (BEAR...
Physician leaders from AdventHealth’s emergency department, infectious disease, inpatient, pediatrics and pharmacy teams all collaborated to develop a respiratory virus testing algorithm to assist...
Thoracic surgeon Colleen Gaughan, MD, and her team at AdventHealth Celebration, recently became one of the first in the country to incorporate targeted imaging agent Cytalux (pafolacianine) as part of...

On the newest Inspiring Wholeness podcast, Obie Diaz, local morning radio show host, shares how a routine physical eventually led to two open heart surgeries.
AdventHealth recently began piloting a new Genomics Risk Assessment for Cancer and Early Detection (GRACE) program that combines the use of digital mammography, artificial intelligence (AI) technology...
AdventHealth Clinical Research Unit (CRU) Executive Director and Medical Director of Genitourinary Oncology Guru Sonpavde, MD, co-authored an article on the AMBASSADOR Phase III clinical trial results...
